New Android virus uses text messages
Posted by: Jon on 05/25/2013 06:52 AM
[
 Comments
]
Comments
]
Dr. Web has identified a new Trojan virus that specifically targets Android, it will intercept inbound short messages and forward them to criminals.
When the malware is started by careless users, the Android.Pincer Trojans display a message about supposedly successful installation of a security certificate to the mobile device. This malicious program is spread as a security certificate that supposedly must be installed onto an Android device.
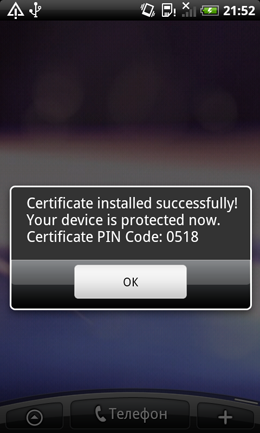
Dr. Web outlines that Android.Pincer.2.origin will display a fake notification about the certificate’s successful installation and will not perform any noticeable activities for a while.
Dr. Web also notes that if at some point Android.Pincer.2.origin is launched successfully at startup, it will connect to a remote server and send it information about the mobile device, including:
Handset model
Device's serial number
IMEI
Carrier
Cell phone number
Default system language
Operating system
Availability of the root account
After that, the program awaits instructions that contain commands in the following format: "command:[command]". The following directives can be sent to the malware by criminals:
start_sms_forwarding [telephone number]— begin intercepting communications from a specified number
stop_sms_forwarding — stop intercepting messages
send_sms [phone number and text] — send a short message using the specified parameters
simple_execute_ussd — send a USSD message
stop_program—stop working
show_message—display a message on the screen of the mobile device
set_urls - change the address of the control server
ping - send an SMS containing the text 'pong to a previously specified number
set_sms_number—change the number to which messages containing the text string 'pong' are sent.
The command start_sms_forwarding is of particular interest since it allows attackers to indicate the number from which the Trojan needs to intercept messages. This feature enables criminals to use the Trojan for targeted attacks and steal specific messages, for example, those received from banking services and containing mTAN codes or other messages containing sensitive information.
When the malware is started by careless users, the Android.Pincer Trojans display a message about supposedly successful installation of a security certificate to the mobile device. This malicious program is spread as a security certificate that supposedly must be installed onto an Android device.

Dr. Web outlines that Android.Pincer.2.origin will display a fake notification about the certificate’s successful installation and will not perform any noticeable activities for a while.
Dr. Web also notes that if at some point Android.Pincer.2.origin is launched successfully at startup, it will connect to a remote server and send it information about the mobile device, including:
Handset model
Device's serial number
IMEI
Carrier
Cell phone number
Default system language
Operating system
Availability of the root account
After that, the program awaits instructions that contain commands in the following format: "command:[command]". The following directives can be sent to the malware by criminals:
start_sms_forwarding [telephone number]— begin intercepting communications from a specified number
stop_sms_forwarding — stop intercepting messages
send_sms [phone number and text] — send a short message using the specified parameters
simple_execute_ussd — send a USSD message
stop_program—stop working
show_message—display a message on the screen of the mobile device
set_urls - change the address of the control server
ping - send an SMS containing the text 'pong to a previously specified number
set_sms_number—change the number to which messages containing the text string 'pong' are sent.
The command start_sms_forwarding is of particular interest since it allows attackers to indicate the number from which the Trojan needs to intercept messages. This feature enables criminals to use the Trojan for targeted attacks and steal specific messages, for example, those received from banking services and containing mTAN codes or other messages containing sensitive information.
Comments






