State of the Internet Report (Security, internet and mobile)
Posted by: Timothy Tibbetts on 07/24/2013 02:58 PM
[
 Comments
]
Comments
]
Each quarter, Akamai publishes its "State of the Internet" report, based on data gathered across Akamai’s global server network. "State of the Internet" highlights attack traffic, connection speeds, Internet penetration, broadband adoption, and mobile usage, as well as trends seen in this data over time.
as well as trends seen in this data over time. In addition, this edition of the report includes insight into so-called “account checker” attacks that targeted e-commerce sites, the states
of IPv4 exhaustion and IPv6 adoption, Internet “events” and disruptions that occurred during the quarter, and observations from Akamai partner Ericsson on data and voice traffic growth
on mobile networks.
Security
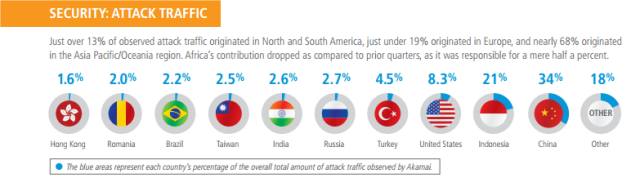
During the first quarter of 2013, Akamai observed attack traffic originating from source IP addresses in 177 unique countries/regions. Note that our methodology captures the
source IP address of an observed attack, and cannot determine attribution of an attacker. China’s share of attack traffic fell to 34% during the quarter, while Indonesia’s grew from near
zero to over 20%. Attack traffic from the United States fell from 10% to just over 8%. Attack traffic concentration grew significantly from the fourth quarter of 2012, with the top 10
ports seeing 80% of observed attacks. Significant growth was seen in attacks targeting Ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (SSL), most of which came from Indonesia. During the first quarter of 2013,
Akamai’s customers reported being targeted by 208 DDoS attacks, up 4% from the prior quarter. Enterprise customers were most frequently targeted, hit by 35% of the attacks. In
addition, during the first quarter Akamai observed attempted account takeover behavior for a number of merchants resulting from reuse of credentials obtained from other sites.
Internet and Broadband Adoption
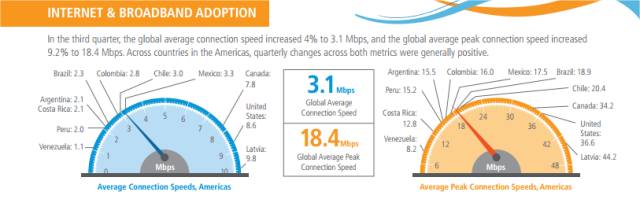
Akamai observed a 3.1% increase in the number of unique IPv4 addresses connecting to the Akamai platform, growing to nearly 734 million, or approximately 34 million more than were seen in the fourth quarter of 2012. Looking at connection speeds, the global average connection speed climbed 4.0% to 3.1 Mbps, and the global average peak connection speed increased 9.2% to 18.4 Mbps. At a country level, South Korea had the highest average connection speed at 14.2 Mbps, while Hong Kong once again had the highest average peak connection speed at 63.6 Mbps. Globally, high broadband (>10 Mbps) adoption grew 10% quarter-over-quarter to 13%, and South Korea remained the country with the highest level of high broadband adoption, growing to 50%. Global broadband (>4 Mbps) adoption grew 5.8% to 46%, with Switzerland taking the top spot with 88% broadband adoption.
Mobile Connectivity
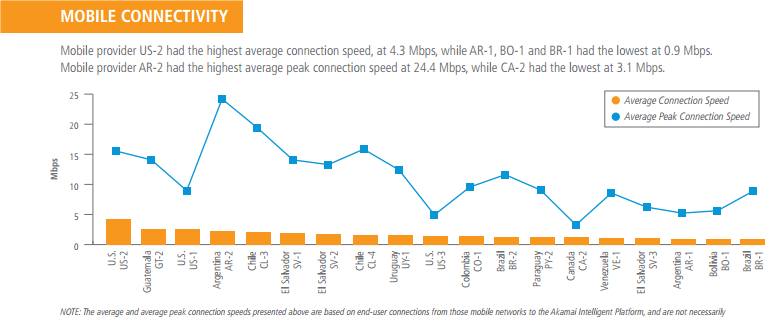
In the first quarter of 2013, average connection speeds on surveyed mobile network providers ranged from a high of 8.6 Mbps down to a low of 0.4 Mbps. Average peak connection speeds ranged from 45.6 Mbps down to 2.8 Mbps. Based on traffic data collected by Ericsson, the volume of mobile data
traffic increased 19% between the fourth quarter of 2012 and the first quarter of 2013, while doubling year-over-year. In contrast, mobile voice traffic grew only 4% during that same
year-over-year period. Analysis of Akamai IO data collected across the first quarter from a sample of requests to the Akamai Intelligent Platform indicates that for users of devices on cellular networks, the largest percentage of requests came from Android Webkit (41-44%), ahead of Apple Mobile Safari (30-38%). However, for users of mobile devices across all networks (not just cellular), Apple Mobile Safari accounted for approximately 60%, with Android Webkit responsible for 20-33% of requests. (The ranges are related to updates made to the back-end data
source in the middle of the quarter.)
If you made it this far, the entire report is available here.
as well as trends seen in this data over time. In addition, this edition of the report includes insight into so-called “account checker” attacks that targeted e-commerce sites, the states
of IPv4 exhaustion and IPv6 adoption, Internet “events” and disruptions that occurred during the quarter, and observations from Akamai partner Ericsson on data and voice traffic growth
on mobile networks.
Security

During the first quarter of 2013, Akamai observed attack traffic originating from source IP addresses in 177 unique countries/regions. Note that our methodology captures the
source IP address of an observed attack, and cannot determine attribution of an attacker. China’s share of attack traffic fell to 34% during the quarter, while Indonesia’s grew from near
zero to over 20%. Attack traffic from the United States fell from 10% to just over 8%. Attack traffic concentration grew significantly from the fourth quarter of 2012, with the top 10
ports seeing 80% of observed attacks. Significant growth was seen in attacks targeting Ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (SSL), most of which came from Indonesia. During the first quarter of 2013,
Akamai’s customers reported being targeted by 208 DDoS attacks, up 4% from the prior quarter. Enterprise customers were most frequently targeted, hit by 35% of the attacks. In
addition, during the first quarter Akamai observed attempted account takeover behavior for a number of merchants resulting from reuse of credentials obtained from other sites.
Internet and Broadband Adoption

Akamai observed a 3.1% increase in the number of unique IPv4 addresses connecting to the Akamai platform, growing to nearly 734 million, or approximately 34 million more than were seen in the fourth quarter of 2012. Looking at connection speeds, the global average connection speed climbed 4.0% to 3.1 Mbps, and the global average peak connection speed increased 9.2% to 18.4 Mbps. At a country level, South Korea had the highest average connection speed at 14.2 Mbps, while Hong Kong once again had the highest average peak connection speed at 63.6 Mbps. Globally, high broadband (>10 Mbps) adoption grew 10% quarter-over-quarter to 13%, and South Korea remained the country with the highest level of high broadband adoption, growing to 50%. Global broadband (>4 Mbps) adoption grew 5.8% to 46%, with Switzerland taking the top spot with 88% broadband adoption.
Mobile Connectivity

In the first quarter of 2013, average connection speeds on surveyed mobile network providers ranged from a high of 8.6 Mbps down to a low of 0.4 Mbps. Average peak connection speeds ranged from 45.6 Mbps down to 2.8 Mbps. Based on traffic data collected by Ericsson, the volume of mobile data
traffic increased 19% between the fourth quarter of 2012 and the first quarter of 2013, while doubling year-over-year. In contrast, mobile voice traffic grew only 4% during that same
year-over-year period. Analysis of Akamai IO data collected across the first quarter from a sample of requests to the Akamai Intelligent Platform indicates that for users of devices on cellular networks, the largest percentage of requests came from Android Webkit (41-44%), ahead of Apple Mobile Safari (30-38%). However, for users of mobile devices across all networks (not just cellular), Apple Mobile Safari accounted for approximately 60%, with Android Webkit responsible for 20-33% of requests. (The ranges are related to updates made to the back-end data
source in the middle of the quarter.)
If you made it this far, the entire report is available here.
Comments





