MBR or GUID? How Should You Partition Your Drive?
By Corporal Punishmenton 08/18/2022 |
Two primary partitioning schemes that can be used on a hard drive: MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table). So, which one should you use?
The answer depends on a few factors, including the operating system you're using and the size of your hard drive. Here's a look at the pros and cons of each scheme to help you make the best decision for your needs.
First, the drive partition should not be confused with the file system. The partition is the container you choose, and the file system is the method of organizing the data in the container (NTFS, FAT EX, etc.)
MBR (Master Boot Record)
MBR is the older of the two partitioning schemes. It's been around since the early days of personal computing, and it's still used on many computers today. MBR has a few advantages:
- It's compatible with a wide range of operating systems, including older versions of Windows, Linux, and BSD.
- It can be used on hard drives up to 2TB in size.
However, MBR also has a few disadvantages:
- It's limited to four primary partitions. If you want more than four partitions, you'll need to create an extended partition and logical drives within that partition.
- It doesn't support drives larger than 2TB.
- It's not as resilient to data corruption as GPT.
GPT (GUID Partition Table)
GPT is the newer partitioning scheme, and it's slowly becoming the standard for new computers. GPT has a few advantages over MBR:
- It supports an unlimited number of partitions.
- It's more resilient to data corruption.
- It can be used on drives larger than 2TB.
- A wide array of Operating systems supports it; Free BSD, Linux, macOS, and Solaris newer versions of Windows.
However, GPT also has a few disadvantages:
- It's not compatible with all operating systems.
- Some versions of macOS and x86 architecture Windows support booting from GPT partitions only on systems with EFI firmware
- It requires a UEFI-compatible motherboard.
You can change between the two if needed. If you have an old drive partitioned as MBR, you can convert it to the newer GPT because you now have a new system that you want to load Windows on; it is possible by using DiskPart. But be careful to know the exact drives on which you are working. You WILL be erasing the drive(s). So either back it up first or prepare to get very acquainted with our Data Recovery section.
Here's how you would do it - be careful.
Open the Command prompt and type 'diskpart" and enter.
Get the number of the drive you wish to reformat and type
Select disk
clean
convert gpt
exit
then let the OS do its thing.
Diskpart will also show you if your drive is already partitioned as GPT. As you can see in this screenshot, Disk 0 and Disk 1 are already GPT on the system.
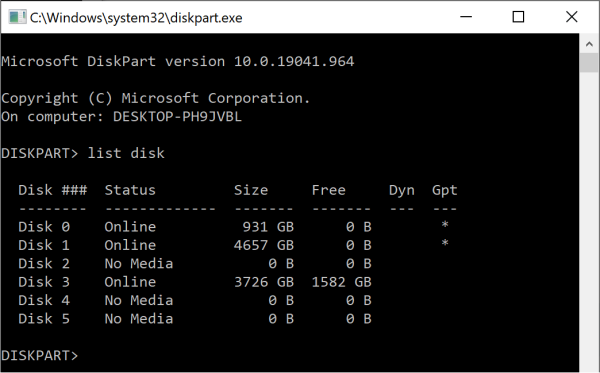
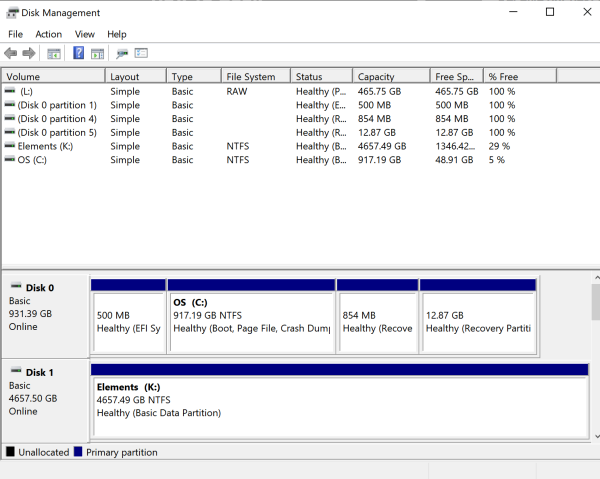
You can also do this with the disk management tool in Windows (hit WIN+R and run diskmgmt.msc)
You must remove the partition of the drive you wish to work with first. Then right-click that drive and choose "Convert to GPT Disk" or "Convert to MBR Disk."
So, which partitioning scheme should you use? If you're using a newer computer with a UEFI-compatible motherboard and want to use all of the features of your hard drive, then GPT is the way to go. If you're using an older computer or need compatibility with a broader range of operating systems, then MBR is probably the better choice.
comments powered by Disqus
The answer depends on a few factors, including the operating system you're using and the size of your hard drive. Here's a look at the pros and cons of each scheme to help you make the best decision for your needs.
First, the drive partition should not be confused with the file system. The partition is the container you choose, and the file system is the method of organizing the data in the container (NTFS, FAT EX, etc.)
MBR (Master Boot Record)
MBR is the older of the two partitioning schemes. It's been around since the early days of personal computing, and it's still used on many computers today. MBR has a few advantages:
- It's compatible with a wide range of operating systems, including older versions of Windows, Linux, and BSD.
- It can be used on hard drives up to 2TB in size.
However, MBR also has a few disadvantages:
- It's limited to four primary partitions. If you want more than four partitions, you'll need to create an extended partition and logical drives within that partition.
- It doesn't support drives larger than 2TB.
- It's not as resilient to data corruption as GPT.
GPT (GUID Partition Table)
GPT is the newer partitioning scheme, and it's slowly becoming the standard for new computers. GPT has a few advantages over MBR:
- It supports an unlimited number of partitions.
- It's more resilient to data corruption.
- It can be used on drives larger than 2TB.
- A wide array of Operating systems supports it; Free BSD, Linux, macOS, and Solaris newer versions of Windows.
However, GPT also has a few disadvantages:
- It's not compatible with all operating systems.
- Some versions of macOS and x86 architecture Windows support booting from GPT partitions only on systems with EFI firmware
- It requires a UEFI-compatible motherboard.
You can change between the two if needed. If you have an old drive partitioned as MBR, you can convert it to the newer GPT because you now have a new system that you want to load Windows on; it is possible by using DiskPart. But be careful to know the exact drives on which you are working. You WILL be erasing the drive(s). So either back it up first or prepare to get very acquainted with our Data Recovery section.
Here's how you would do it - be careful.
Open the Command prompt and type 'diskpart" and enter.
Get the number of the drive you wish to reformat and type
Select disk
clean
convert gpt
exit
then let the OS do its thing.
Diskpart will also show you if your drive is already partitioned as GPT. As you can see in this screenshot, Disk 0 and Disk 1 are already GPT on the system.

You can also do this with the disk management tool in Windows (hit WIN+R and run diskmgmt.msc)
You must remove the partition of the drive you wish to work with first. Then right-click that drive and choose "Convert to GPT Disk" or "Convert to MBR Disk."

So, which partitioning scheme should you use? If you're using a newer computer with a UEFI-compatible motherboard and want to use all of the features of your hard drive, then GPT is the way to go. If you're using an older computer or need compatibility with a broader range of operating systems, then MBR is probably the better choice.
comments powered by Disqus






